Over the past few decades, Brazil has been working towards growing synergy between innovation and sustainability. Thanks to technology and the dedication of hundreds of rural producers, we are proud to offer the world a natural raw material that fully respects the environment and people, through a process of continuous improvement.

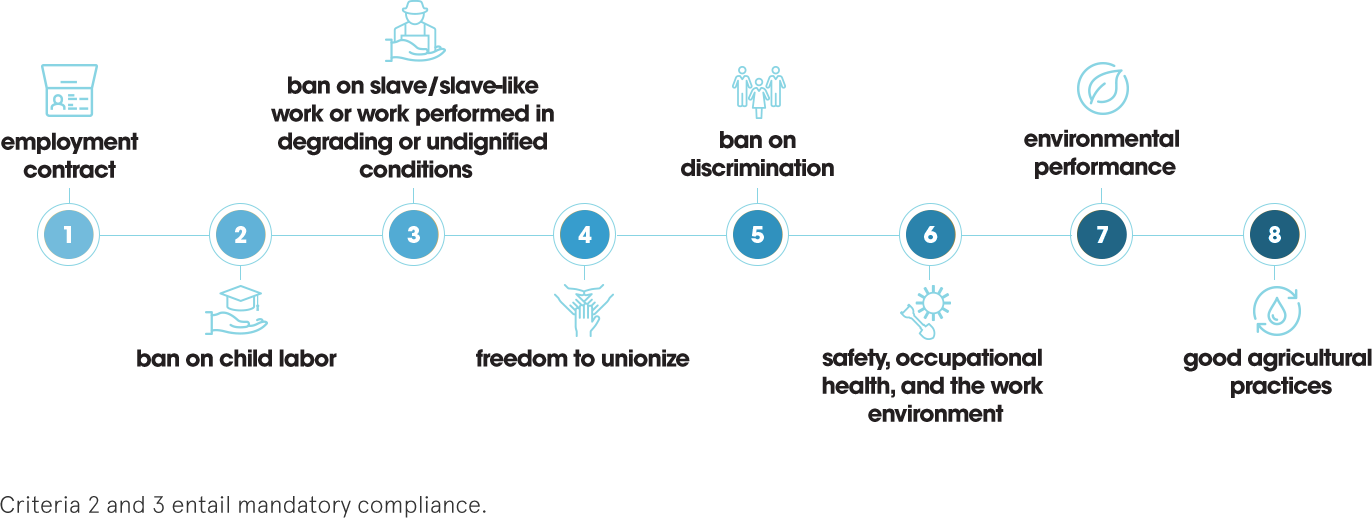
preservation of native fauna and flora, protection of springs and rivers, rational use of pesticides, use of clean and renewable energy, good agricultural practices, and crop rotation.

respect for workers’ health and well-being, promoting fair relationships between employers and employees, and contributing to community development.

prioritizing the economic health of businesses so that all parties, without distinction, can grow together and support the Brazilian macroeconomy.
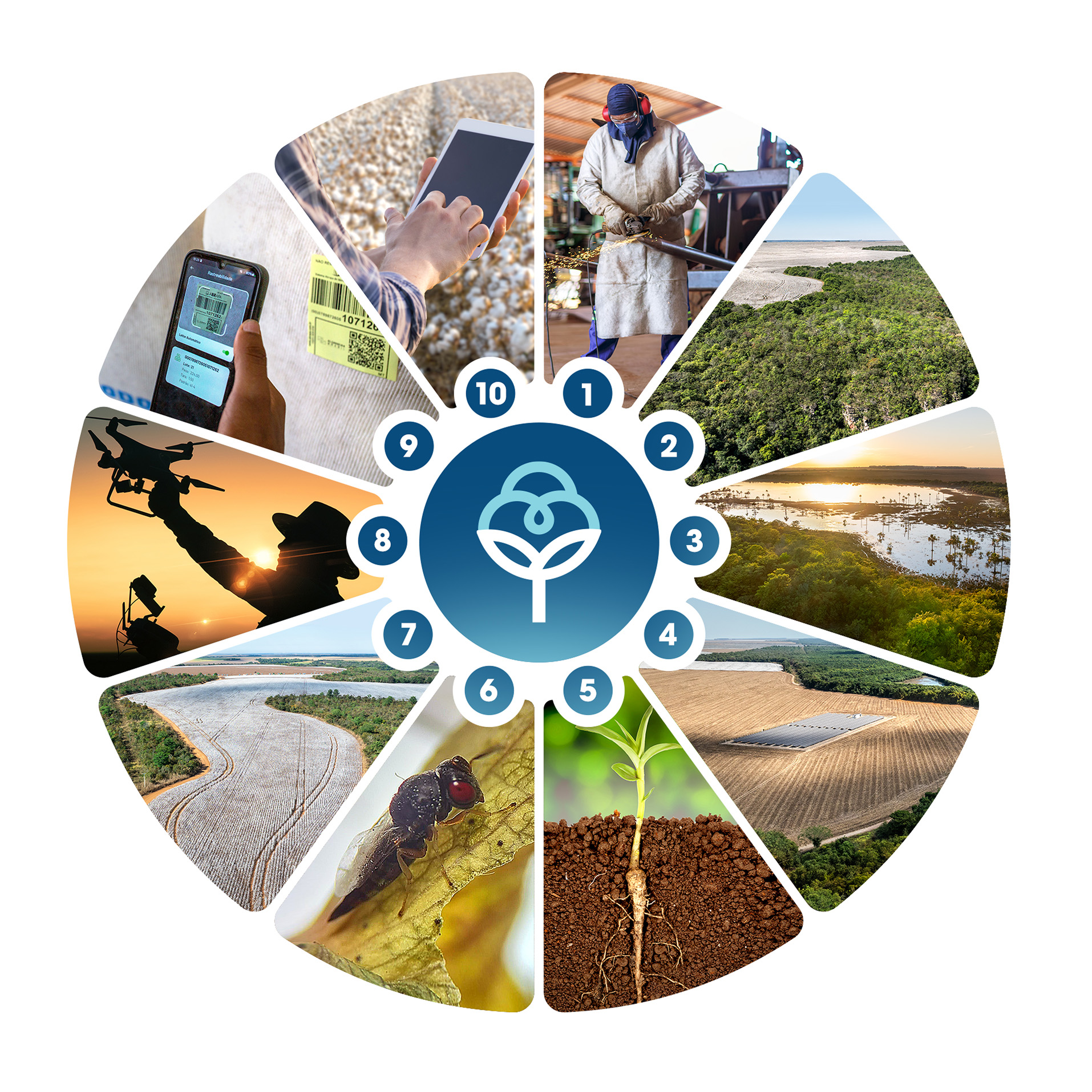
Click to open box with description of each item
1 - worker’s & farmer’s safety and wellbeing
2 - environmental conservation
3 - water Conservation
4 - clean energy
5 - soil protection
6 - Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
7 - land use efficiency
8 - smart farming
9 - transparency & traceability
10 - verified/certified production


In addition to only 8% of the Brazilian fiber being cultivated using irrigation, there are projects for regional conservation of water resources - protection, preservation and recovery of riverheads, studies on silting up and contamination by chemicals – and specifics actions with the study’s results. Ex.: Project: recovery of river springs by rural producers.

Brazil's electricity matrix is based in renewable sources. In 2020, renewable energy supplied 85% of the electricity sector demand and it is expected to reach 88% by 2030. This contributes to reduce the carbon footprint of the cotton supply chain in Brazil.

Encouraging the use of biological pest and diseases control. The objective is to replace part of the chemical pesticides used. Other promoted techniques include: free-host period, biotechnology, mandatory crop calendar, biopesticides, insect traps and scouting, etc.

In Brazil, cotton is produced mostly as a second crop. This is called “double cropping system” and means that once the raining season starts (Sep-Oct) farmers plant soybeans and only after the soybean harvest (Jan-Feb), cotton is seeded. 63% of all cotton production in Brazil is grown as a second crop. In other words, more than 1 million hectares of land are being spared, reducing land use change pressure and maximizing food and fiber production per hectare.

Brazilian farmers are known for the high level of technology adoption in their farms. Smart and digital farming tools have been largely used in order to increase operational efficiency and reduce input use.

Each cotton bale produced in the country has a bale identification number that can be used to trace the bale back to the farm, farmer and cotton gin, using an online database. Abrapa has invested to bring certification and traceability with large financial investments.

Encouraging the use of soil conservationist practices. Cover cropping, no-tillage and reduced tillage are widespread practices among Brazilian cotton growers. In combination with cover crops and crop rotation, these practices improve soil health and contribute to reducing GHG emissions.

In addition to only 8% of the Brazilian fiber being cultivated using irrigation, there are projects for regional conservation of water resources - protection, preservation, and recovery of riverheads, studies on silting up and contamination by chemicals – and specific actions with the study’s results. Example: Project for recovery of river springs by rural producers.

Regularization of environmental conservation areas, in line with the Brazilian Forest code, in all farms; Depending on where a farm is located, between 20% and 80% of the native vegetation of each farm must be preserved by the farmer as well as riparian forests along rivers and streams. Farmers are also engaged in the prevention of farm and wildfires, through the implementation of on farm fire brigades.

Effective reduction of workers accidents due to the training actions implemented by the certification; Improvement of well-being and health of farmers and farm workers; Farm workers are also trained on the correct use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and other safety measures when handling crop protection products and farm equipment.
Cotton production in Brazil relies on the three pillars of sustainability: environmental, social, and economic. In line with the growing demand from consumers who vaule the responsible origin of the raw material. Find out some highlights:

17% higher Human Development Index (HDI) in cotton-producing municipalities
compared to the Brazilian average
41,600 formal direct jobs are created on certified farms

Brazil is the #1 responsible cotton supplier in the world
More than 35% of all cotton licensed by Better Cotton is Brazilian

82% f total national production (3.04m ton of cotton lint) has been audited and approved in terms of sustainability criteria by third-party companies (2023/2024)

2.2x less land use to produce cotton comparing with the global average
BRA: 1.868 kg of lint/hectare
World Average: 827kg of lint/hectare
2024/2025 crop

Over 90% of the crops grow without artificial irrigation, relying on rainfall water instead.
Brazil leads the world in adopting soil conservation practices in certified cotton production
80% with zero tillage planting
The Responsible Brazilian Cotton Program –ABR (its Portuguese abbreviation) –is Brazil’s national certification scheme for responsible cotton production. Created in 2009, the program ensures that every certified bale meets rigorous environmental, social, and economic standards through annual audits conducted by independent, accredited experts.
Download the latest ABR reports here:

The ABR certification protocol brings together the most relevant aspects of Brazil’s labor and environmental legislation combined with the world’s best responsible practices. For this reason, our protocol has been in synergy with Better Cotton from the beginning, in 2013. For a producer to obtain Better Cotton licensing, they must first be ABR certified.
Brazil stands out as number one in Better Cotton supply, setting a new standard for sustainability in the cotton production chain. This reflects our commitment to responsible agricultural practices and strengthening an ethical and efficient supply chain, from cultivation to the global industry.
In recent years, the ABR, existed since 2012, has grown beyond the farms, extending to processing units (ABR-UBA) and retro-port terminals (ABR-LOG).
This marks a step forward in transparency at different stages of the Brazilian production chain and in the continuous improvement of our sustainability efforts.

Since December 2024, Cotton Brazil has been part of the European Make the Label Count coalition, expanding its role in global sustainability guidelines and lending its voice to actions aimed at raw materials’ quality and responsible origin. Together with Anea and Abrapa (Brazilian Cotton Producers Association), the Cotton Brazil membership ensures that the full weight of the Brazilian cotton sector is behind this important effort, affirming Brazil’s commitment to strengthening and defending the environmental benefits of natural fibers such as cotton at this critical juncture.

We are delighted to welcome ABRAPA and as a consequence Cotton Brazil to the Make the Label Count coalition. As a globally recognized organization committed to sustainable cotton production, their expertise and leadership will strengthen our collective voice and effort to ensure fair and credible sustainability claims for natural fibres. Beyond the socio-economic importance of raw material production for many cotton farmers, the EU’s PEF methodology must properly address the environmental impact of oil-based materials like polyester, which contribute to massive plastic waste and release microplastics into our waters and soils.
Make the Label Count’s spokesperson
To promote the sustainability practices of cotton production in Brazil in order to provide guarantees to the market.
Every year, participating farmers are instructed to answer, with documents, the questionnaires of the ABR protocol before they receive the auditing. This is the diagnostic stage, which is supervised by the technical staff of each of the nine state associations that make up Abrapa, responsible for direct guidance to rural producers and help them to comply and advance in sustainability requirements. This step is essential for the continuous improvement of the properties participating in the ABR program.
Under these pillars, eight evaluation criteria have been established:
The ABR is trustworthy! Audits are independent and conducted annually on-site by certification bodies accredited to ISO 17065.
Accredited certifiers in 2024: Genesis, ABNT, and Qima (ABR and ABR-UBA); Control Union (ABR-LOG).
Since 2013, the ABR protocol has been equivalent to Better Cotton. Additionally, it is recognized by the FAO and is one of the 15 certifications worldwide selected by Textile Exchange as preferred in the global market.
ABR certification data is provided via a label attached to each bale. Learn more.