quality
quality guides the work of Brazilian producers, researchers, and scientists
With studies and advances in technology, Brazilian cotton presents the necessary level of quality to meet production demands, besides being totally free from contamination and being grown in high-yield areas, ensuring year-round supply.
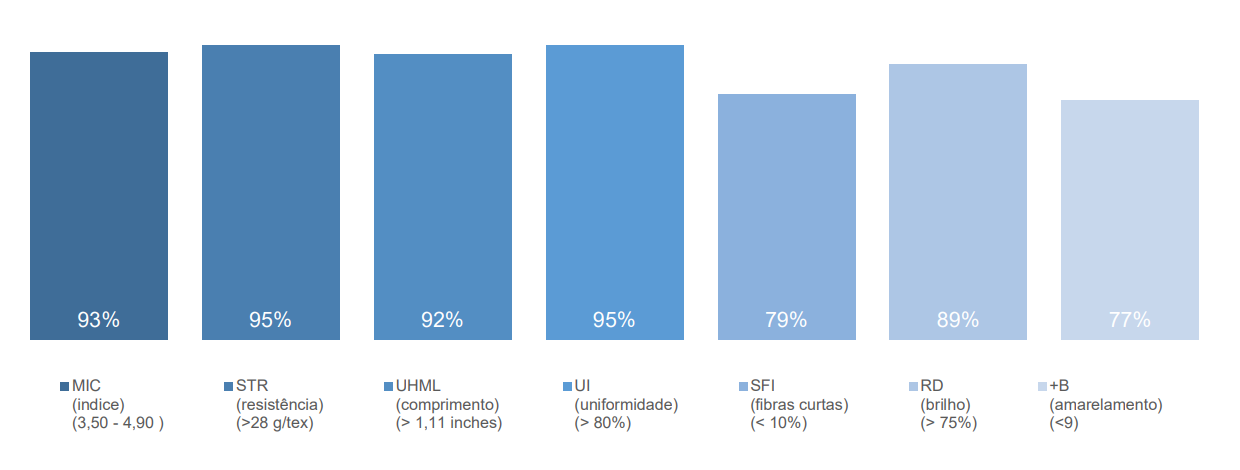
Brazilian cotton Quality indicators – 2023/24
Brazilian Cotton Quality Control Program
In 2016, Abrapa (Brazilian Cotton Growers Association) and its state member associations created the Brazilian Cotton Quality Control Program (SBRHVI) to standardize the instrumental classification of cotton by allowing digital access to cotton test data, and ensuring transparency and credibility to the country’s test results.
SBRHVI comprises a set of practices that promote quality standardization parameters and is based on three pillars:
- Brazilian Reference Center for Cotton Testing (CBRA)
It is the Central lab that monitors all the laboratories through the CBRA Cotton Check program, ensuring the classification processes standardization. CBRA is currently certified by ICA Bremen and accredited by NBR ISO / IEC 17025 high volume instruments analysis.
- Brazilian Cotton Quality Database
An intelligence hub that integrates cotton testing and classification data with the traceability system, and generates the information to be printed on the bar-code labels attached to the bales.
- Guidance to participating laboratories
Training, technical visits, and support for laboratories in Brazil to work at the same quality standards and in line with CBRA.
100% of Brazilian cotton is tested by high-volume instruments (HVI)
For visual and manual classification, two samples are collected from each bale – from opposite sides.
In the 2023/24 season, over 17 million bales was analysed, conducted by 83 machines in 12 Brazilian Labs.
In the classing labs, there is a correct gauging of humidity and temperature for HVI testing and a double colorimeter is used in High Volume Instrument devices to increase the reliability of the reflectance and yellowness data.








